While aiming to optimize a website for different regions and languages, build an SEO strategy using International SEO checklist.
They say in Rome be Roman.
If anyone follows it to the tee are the international companies that offer their product/service across diverse populations. Adapting to multiple geographies, languages, and even cultures.
Similarly, when it comes to optimizing websites for international businesses, your global SEO strategy should focus on localizing what you cater. Shift face in the same body. Meaning, perform — Country-specific SEO and Multilingual SEO while keeping the heart of the website — the domain, steady. And it all starts with an International SEO checklist!

In this guide, we’ll understand the basics of how international search engine optimization works. Then cover the technical bits like ccTLD, hreflang tags, subdirectories and other tinkerings to help structure your international website. We’ll also share expert tips, metrics and tools for International SEO’s success.
Let’s kick off our long journey of the international SEO checklist, with the baby step of defining international SEO itself.
What is international SEO?
International SEO (International Search Engine Optimization) is the process of optimizing a website’s content, structure, and UI/UX elements to improve its SERP (Search Engine Result Page) visibility across target regions and languages.
As touched upon earlier, some of the key elements of international SEO strategy include choosing the right keywords for each country, implementing hreflang tags, and managing the website’s technical infrastructure in a way that localizes the overall website for a target audience.
Clearly, it’s not required for all websites. But is critical for the ones that aim to generate traffic from more than one country or language.
Why is international SEO important?
While the internet leveled the ground of international business expansion (in several aspects), it also highlighted the difference in the online behavior of the populace from different regions. This is backed by the fact that with search engines being primarily text-based directories, there is an inherent requirement for content availability in various languages. Just English won’t do. Plus, the international search engines working with different governments, have come up with dedicated high-level domains (ccTLDs) to provide localized identities to individuals, businesses, and the governments themselves.
Now, when you wish to create an online brand that is identified internationally, you have to weigh in all these factors. And, don’t forget you won’t be the only one competing for the top spot in your niche; there is competition. These are what make international SEO so important.
Difference between local SEO and international SEO
Some of you might still have apprehension as to how different could a global SEO strategy be compared to a local one. Objectively speaking, local SEO and international SEO require different angles of thoughts, efforts, and investment across multiple criteria.
| Criteria | Local SEO | International SEO |
| Audience | Targeted to a specific local audience | Targeted to a global audience across multiple countries |
| Language | Generally limited to a single language | Must account for multiple languages and translations |
| Keywords | Focus on locally relevant keywords and phrases | Requires research and optimization for multiple languages and cultures |
| Backlinks | Emphasis on local business directories and citations | Focus on acquiring quality backlinks from relevant websites globally |
| Pricing | Focus on local pricing and currency | Must account for multiple currencies and pricing in different markets |
With that, we can dive deeper into the checklist for international SEO strategy.
International SEO Best practices checklist
Now, let us look at some of the best SEO international practices that are practiced and appreciated globally.

1. Define website architecture
Whether you are going for multiregional SEO or multilingual SEO, your international SEO strategy begins with deciding the structure of the website i.e. how do you upload content for different audiences under the same domain?
Google recommends three options for international website structure as mentioned below:
Country code top-level domain name (ccTLD)
A ccTLD is a domain name extension that is specific to a country or territory.
Example:
airbnb.co.uk for the United Kingdom
airbnb.de for Germany
airbnb.jp for Japan
To implement this architecture, a business would need to purchase and set up separate domain names for each country which is subject to availability and local laws. So, you should consider using ccTLDs when targeting a range of countries if the focus is to establish a strong local identity, but should weigh the costs of maintaining multiple domains.
Subdomains
A subdomain is part of a website URL that allows for the creation of a separate site or portal specifically for a country or language.
Example:
https://zh.wikipedia.org for China
https://it.wikipedia.org for Italy
https://es.wikipedia.org for Spain
To implement subdomain architecture, you would need to create subdomains for each country or language and optimize each one individually for SEO. But before you do, note that it is a good choice for companies looking to establish sites as separate identities while retaining overall branding and targeting different languages in one country, but may be less trustworthy and require separate link-building campaigns.
Subdirectories
Possibly the easiest to set of them all in website architecture, a subdirectory is a subfolder on a website that is used to organize content.
Example:
https://www.netflix.com/ar/ for Argentina
https://www.netflix.com/kr/ for South Korea
https://www.netflix.com/tr/ for Turkey
You can implement this to create subdirectories for each country, language and even both of them together like:
https://www.example.com/ca/en/ – English language version of the website for Canada.
https://www.example.com/ca/fr/ – French language version of the website for Canada.
So, use subdirectories when targeting multiple languages in a single country, for easy setup and low maintenance, but consider the challenges of low geo-targeting signals and separation of sites.
Interestingly, you can target different languages used in one country in conjunction with subdirectories, e.g. https://ca.example.com/fr and https://ca.example.com/en. However, expert SEOs advise against it for complications of report tracking, and maintenance.
For a comparison of the three website architectures for your international SEO strategy, check out the Matt Howells-Barby SearchLeeds slides[1].
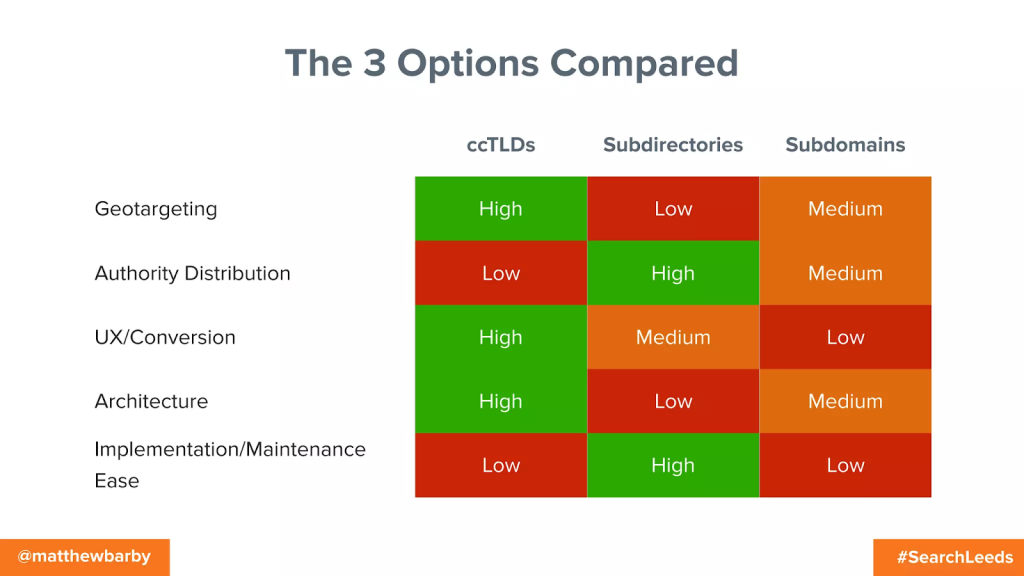
Choosing the right URL structure for your business is like choosing a life partner. You won’t necessarily see immediate negative effects, but picking the wrong one can cost you time and money in the long run. So, choose wisely and commit to it!
2. Consider the HTML and SEO tags
As the next important step of planning an international SEO strategy, understand and utilize the full array of technical SEO tactics in HTML – the language websites are built in. These tags need to be placed as HTML link element(s) in the header of each page of each version of your international website.
- HrefLang tags
You may have heard how of hreflang tags regarding international SEO already. And for a good reason: As hreflang tag help search engines understand which language versions of a page to display for a particular user based on their location and language preference.
Example: <link rel=”alternate” hreflang=”en-US” href=”https://www.example.com/” />.
You can use a hreflang generator to automate this process in case of large-scale page development.
- X default tag
This tag is used to indicate the default version of a page when no language or region is specified. It’s helpful for websites with multiple language versions, as it ensures that users who don’t have a specific language or location preference are directed to the correct version of the page.
Example: <link rel=”alternate” hreflang=”x-default” href=”https://www.example.com/” />.
- Content-language tags
Often sipped but still an important one, content-language tags specify the primary language of the content on a webpage.
Example: <html lang=”en-US”>.
- Schema markup
This is an interesting one — Schema markup is a type of microdata that helps search engines understand the content element and flow on a webpage. It can be added to highlight ratings, events, products for sale, etc.; especially, local business office details from an international SEO angle.
It’s also worth noting that Google supports a variety of languages for Schema markup. But as best practice, use the one that matches the primary language of the content on the page.
3. Host content locally for faster load times
A critical ranking factor Google considers is page speed – the faster the website loads the better. However, when it comes to hosting the website, the more the distance from the server to the user, the higher the loading speed. In addition, your website response times also get affected by slow-loading videos, graphics or large files.
Considering these, for an international website targeting audiences spread across distant geographies, you should look into setting-up local web hosting or CDNs (Content Distribution Networks) as the global web hosting solutions.
4. Conduct keyword research for target markets
In English, “smoking” refers to the act of inhaling smoke typically from a cigarette. However, in French, “le smoking” means “tuxedo”! So if you’re in France and looking to rent formal wear for a fancy event, make sure you ask for “un smoking”.
May be funny in certain contexts but for search engines it may be misleading. So, do your keyword research thoroughly. In fact, it’s highly recommended that outsource this to native speaker(s) or a professional translation service instead of relying on an online translation tool. Not only will it help you accurately target the right audience for your services, but also bring up insights into which markets are already showing interest in your online content.
Do note that while you can begin keyword research in English (or your native language) for ideation, keywords in other languages should never be translated. Transcreate instead.
5. Localize content to appeal to local audiences
What an American imagines by the term ‘bathroom’, a Canadian, does so by ‘washroom’. Whereas folks from the UK would generally call it ‘lavatory’. All speak English, but when talking to them if you don’t speak their English, you might step on their toes. That’s the power of content localization.
So, make this a standard practice of international search engine optimization to get your content vetted by a native language speaker before putting it live. That could mean everything from images, voiceovers, ad copy, website articles and even uses of colors are elements that need to be considered from a local perspective. In case of budget or bandwidth issues, you may refer to forums like WordReference.com[2].
6. Write Metadata for each language
When building an international website, it’s important not to overlook metadata content. This information tends to be evaluated by the audience subconsciously to decide whether to click on a website link on SERP or not. SEOs even go on to say that Meta titles and descriptions are like free ad opportunities offered by Google.
So, sticking to the rules of the meta content length is not enough; you need to master the art of crafting concise and catchy metadata in multiple languages. This becomes especially crucial on e-commerce sites where you have hundreds of product pages that are similar in nature. You may not be penalized for using a template for metadata but definitely will be for not nailing the language.
7. Prioritize user experience for international visitors
Having emphasized enough on the language aspect of the content for international SEO, it makes sense to extend it to over user experience as well. This means making sure that your website is easy to navigate, loads quickly, and provides a seamless experience for users, regardless of their location.
Some quick actionable for improving UX for international visitors include:
- Be mobile-friendly for global users
- Consider culture in design and layout
- Offer local payment and shipping options
8. Monitor and measure results to manage better
The impact of all efforts for international SEO strategy needs to be tracked for proper maintenance of the website. There are lots of nuts and bolts than a local website, so it also becomes an important question that whether to have a single tracking code or multiple tracking codes for each subfolder/subdomain. It’s recommended that you use one tracking code and segments/filters in Google Analytics if subfolders are the same. But if the content is on separate subdomains/subfolders differs or multiple TLDs are running simultaneously, go with multiple tracking codes.
In either case, the basic SEO metrics for international SEO tracking include traffic, bounce rate, conversion rates, and engagement. However, you should also measure all goal-related metrics for the overall website as well as it may point out to a business opportunity.
Tips for successful international SEO
Here are a few tips and tricks for successful international SEO.
1. Don’t rely on automated translations
Even with ChatGPT and other smart translation tools, you can only go so far, so fast. Do not risk offending or being mocked for translation errors as it can negatively impact user experience and search engine optimization. May also create a nuisance to deal with online. Instead, invest in human translation services or hire in-country writers for your target markets.
2. Go beyond Google search engine (Vertical Search)
Google is synonymous to search in most parts of the world but some large markets prefer different search engines: Baidu is the most widely used search engine in China, while Yandex is popular in Russia. Do take these into account when working on country-specific SEO. In addition, vertical search engines like Amazon, LinkedIn and TripAdvisor are also carving their niche that’s worth taking a shot at.
3. Leverage local directories and review sites
Link building is like online word of mouth. Nothing better than to pull in visitors and signal search engines of your authority in your niche. So, get your business listed on popular local directories and review sites. For example, in Japan, Yahoo! Local is a popular directory, while in France, PagesJaunes is widely used. Do it yourself, pay for it and even encourage your customers to leave reviews to improve your local search rankings.
4. Promote with social media, event appearances, & ads
For raising traffic, content promotion is as important as content creation. So, include niche online forums, targeted ads, participation in local events, etc. as part of your global SEO strategy. And, of course, social media. In addition to the seemingly omniscient ones (Instagram, Snapchat, LinkedIn, etc.), get active on the ones popular in your target region e.g. Weibo in China, LINE in Japan, and VKontakte in Russia.
5. Look for local trends for opportunities
When promoting content for international SEO, it’s essential to look for local trends that can help your content go viral. By identifying what’s popular or trending in a particular market, you can create content that resonates with local audiences and increases your chances of reaching a wider audience. For example, during the holiday season, brands can create content that features local traditions or customs to appeal to audiences in different countries.
Tools for international SEO
Knowing international SEO best practices is as much important as knowing how to implement them. Especially when there are various audits, research and tracking required, it’s impossible without international SEO tools. And for various items in the international SEO checklist, there are different tools. Some of the most popular and trusted ones we discuss below:
1. Semrush
Semrush is a popular all-in-one digital marketing tool that provides a comprehensive suite of features for international SEO. They even have a stepwise recommendation on international SEO[3] that starts from using ‘Site Audit Tool’ to finding hreflang mistakes to all the way to improving on-page SEO with their proprietary ‘On-Page SEO Checker’.
2. Ahrefs
From using ‘Site Explorer’ to decide on the potential of entering a new market, to reviewing hreflang implementation with ‘Site Audit’, Ahrefs is a powerful tool for international SEO. Their ‘Keywords Explorer’ is also quite useful for keyword research in several languages that also ‘suggests matching terms’, ‘questions’, ‘also rank for’, ‘and also talk about’.
3. MOZ
In addition to the keyword research, competition audit, and link explorer tools, Moz’s industry-defining metrics viz. MozRank and Domain Authority sets it apart among the international SEO tools. In addition, its MozBar Premium helps get instant page optimization suggestions for keywords in any language on any page.
Now, you may ask ‘Which is the best international SEO tool?
Answer: None.
It all depends on your business objectives, your understanding of international SEO, and your budget. All three (and more) are great tools, but it’s in the hand of SEO to make the most of it.
Related Reads:
Concluding Notes On International SEO Checklist
With that, this international SEO checklist covers everything you need to get started with your global SEO strategy.
Now, as you go about inserting tags, creating content, and using SEO tools, remember: The world is a diverse place. For organizations catering their product/service online across regions, International SEO strategy is both science and art. And localization is at the heart of both.
Bookmark this checklist to come back anytime you need help with international search engine optimization!
FAQs– International SEO Checklist
International SEO is different as it requires optimizing a website for multiple countries and languages, taking into account cultural nuances.
Multi-regional SEO targets specific regions or countries, with local content and domain structure.
A multilingual website has content in multiple languages, targeting users who speak different languages.
Multilingual SEO targets different languages, while multi-regional SEO targets different regions or countries.
Hreflang is an HTML attribute used to indicate language and regional targeting for search engines.
To take an example of a hreflang tag consider a page targeting French speakers in Canada:
<link rel=”alternate” href=”http://example.com/fr-ca” hreflang=”fr-ca” />
References
[3] https://www.semrush.com/blog/guide-how-to-do-international-seo-with-semrush/


